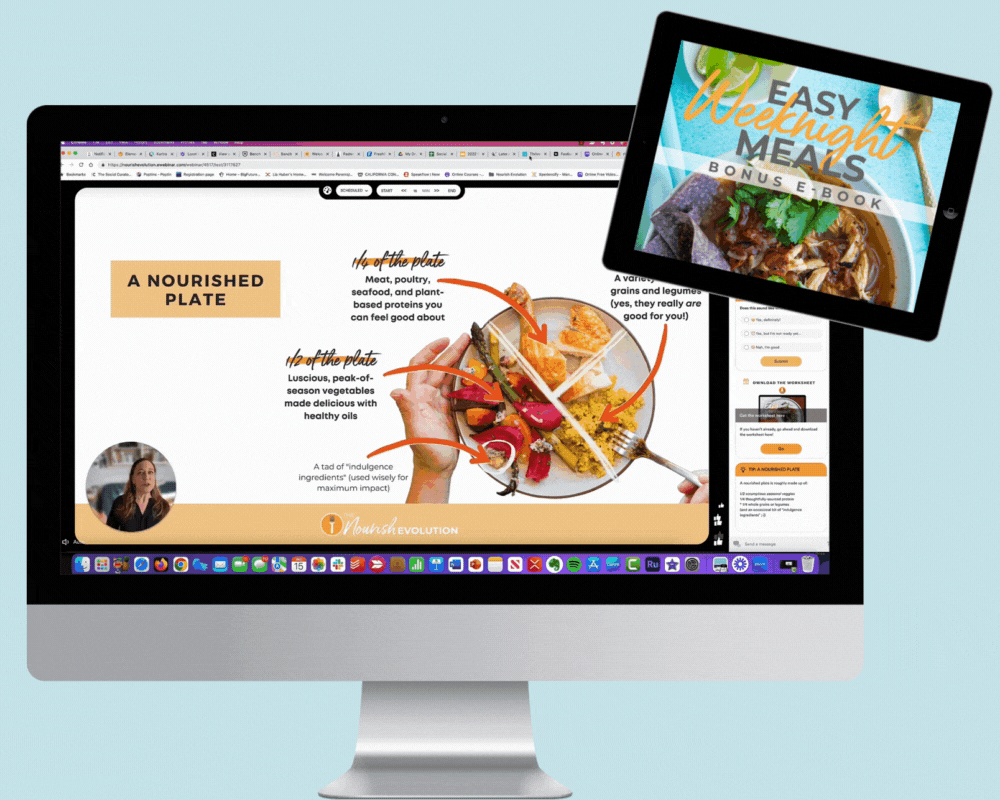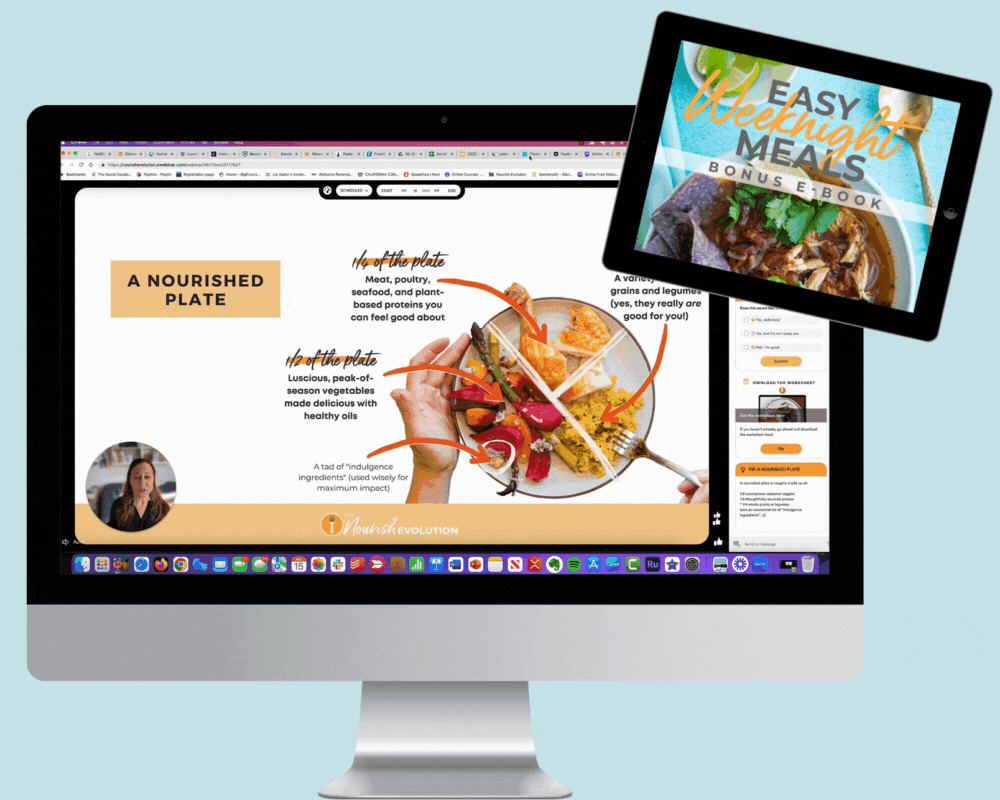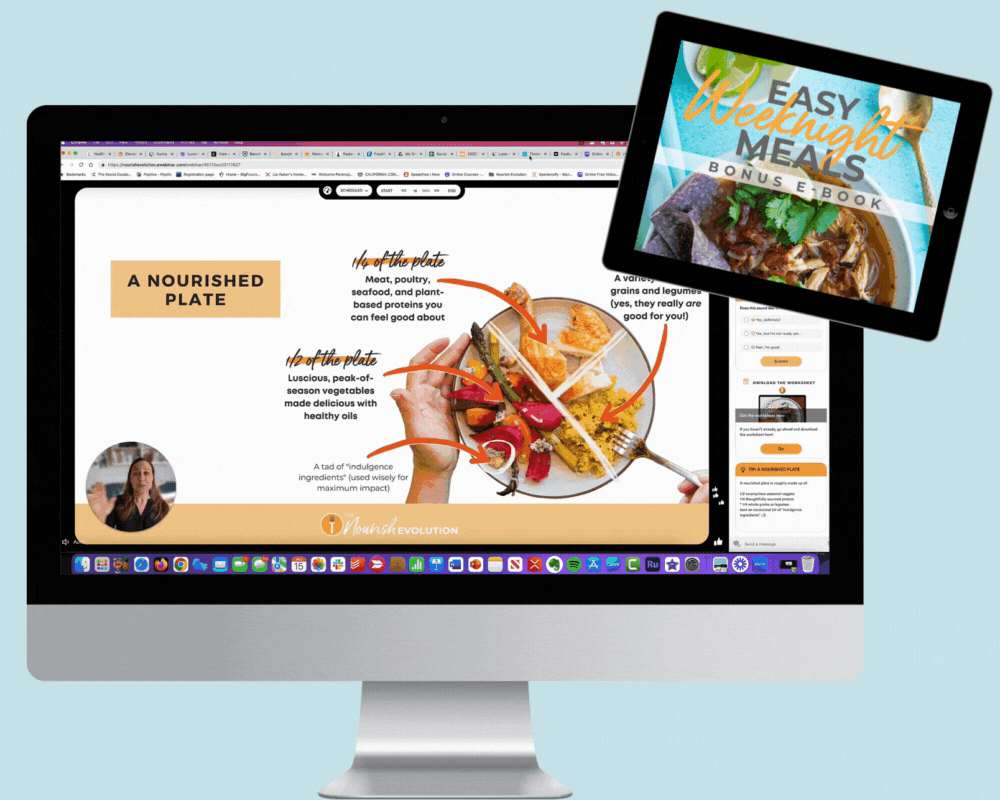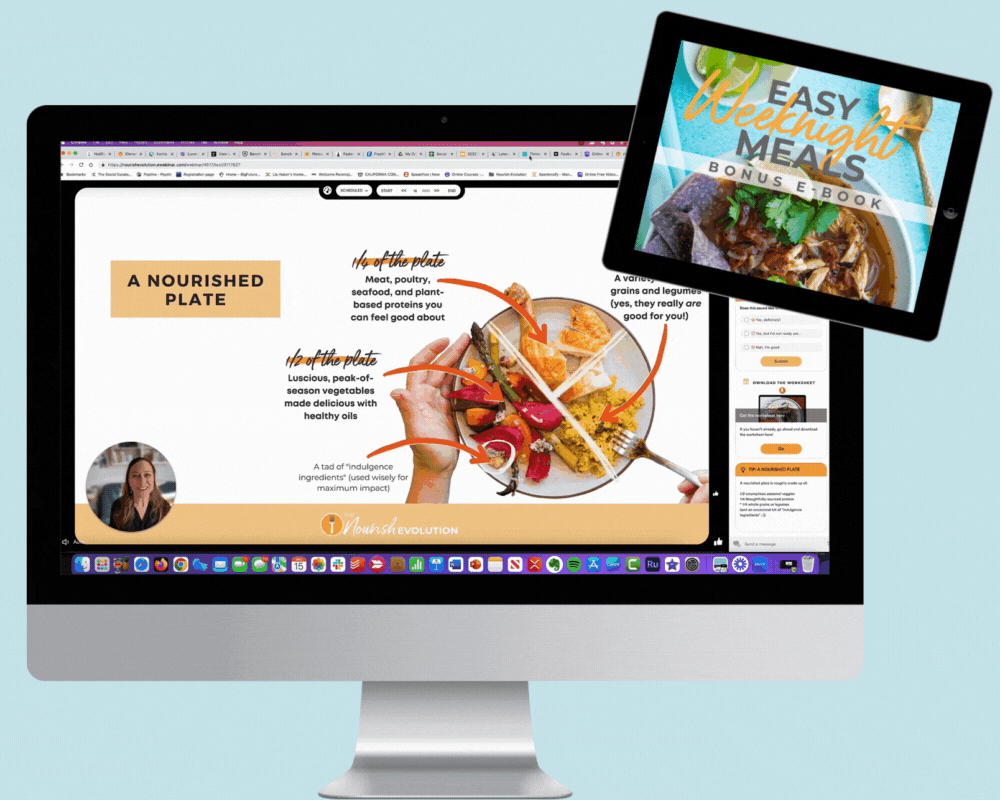
If you’re confused about farmed fish, you are not alone. Aquaculture — fish farming — is hailed by some as the saving grace to our future fish supply and called an ecological disaster by others. What makes it so complex an issue is that, depending on what they’re referring to, both parties are right. What's not in question is that aquaculture is here to stay; half of the seafood eaten by Americans today is farmed, and the number continues to rise. And, done right, it can be part of a sustainable seafood solution. Here are four basic guidelines to clarify which farmed fish are best to buy and why:
- Best choice. Mussels, oysters and clams. Why? Not only do these mollusks filter the water they’re raised in so that it’s cleaner than it was before they arrived (they feed on tiny, floating plankton), they are also an impetus for communities to conform to strict clean water regulations wherever farms are located.
- Good choice. Tilapia, barramundi, catfish, striped bass, arctic char, trout and shrimp. Why? These fish are good choices for aquaculture because they are omnivores—they eat both plants and animals—or, in the case of tilapia, herbivores. Many experts view new technology, called Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS), as the gold standard in aquaculture, providing both a pristine environment for the fish and a completely closed system to avoid polluting native species nearby.
- Worst choice. Salmon. Why? Primarily because the species itself is carnivorous—it takes 8 pounds of wild fish to make 1 pound of salmon—which makes it a poor choice for farming. But also because most salmon is farmed off-shore in net-pens, which can pollute the waters around them and cause unnervingly high levels of toxins, disease and parasites in the fish. What’s more, these farmed fish occasionally escape, spreading disease to native populations and putting the gene pool of wild species at risk.
- Know your sources. With the Country of Origin Labeling Act (COOL ) enacted in 2005, the US government gave consumers the right—and the ability—to know where our seafood comes from. And that’s a good thing, given that there are no international standards for the sustainability and safety of aquaculture operations. There are laws governing the environmental impact for fish farms in the United States, yet in other countries, like Thailand and China, aquaculture has had a devastating effect on coastal eco systems. New international standards are being developed, but right now, your best bet is to avoid imported farmed fish and shrimp altogether unless from credible suppliers you know are committed to sustainability.